In the world of coffee, there is an intriguing process that takes place behind the scenes—roasting. Roasting coffee beans is a captivating journey that unlocks the hidden potential and flavors encapsulated within the unassuming raw coffee seeds.
Whether you are a coffee enthusiast, a passionate drinker, or simply curious about the intricacies of this captivating process, join us today as we delve into the world of coffee roasting.
Covering everything from the impact of roasting on taste to the chemistry unfolding within the coffee beans, we aim to unravel the mysteries and provide insights into the terminology used by roasters.
We will explore the different types of machines employed by specialty coffee companies, as well as the meticulous processes they undertake to ensure a consistently delightful coffee experience. But before we embark on this exciting journey, let’s start where it all begins—with raw coffee.
Raw Coffee: The Unassuming Beginning
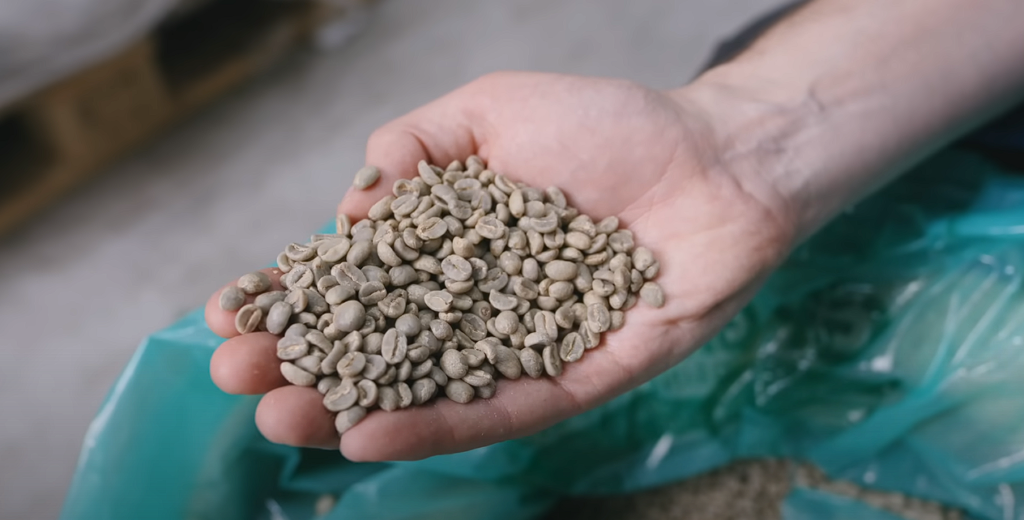
At the genesis of the coffee-roasting process lies raw coffee, dried seeds obtained from the coffee tree. Raw coffee possesses a rather unimpressive aroma and taste, resembling plant seeds more than the rich and complex flavors we associate with coffee. However, it is during the roasting process that a mesmerizing transformation occurs within these unassuming beans, releasing a world of flavors and complexities that one would never expect.

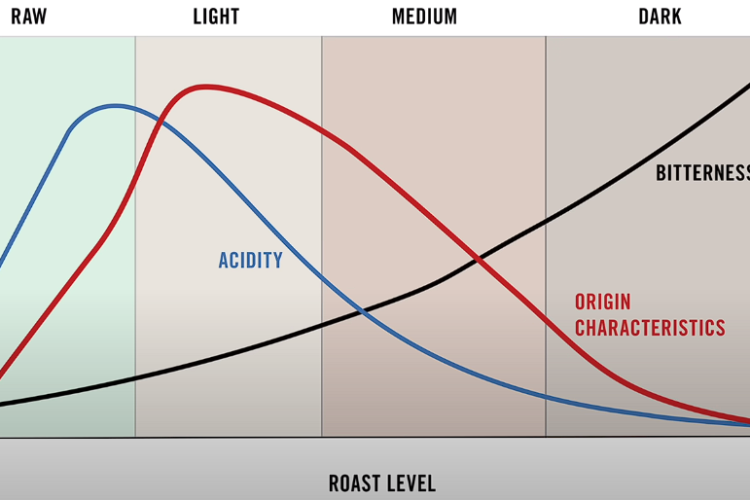
Understanding the Impact of Roasting: Bitterness, Acidity, and Origin Characteristics
The roasting process plays a pivotal role in crafting the familiar coffee flavors we all cherish. Simplifying the complex nature of roasting, three key characteristics come into play: bitterness, acidity, and origin characteristics. As coffee beans are roasted for longer duration, their color darkens, resulting in an increase in bitterness. Acidity, on the other hand, initially intensifies, reaches a peak, and then diminishes as the roast darkens.
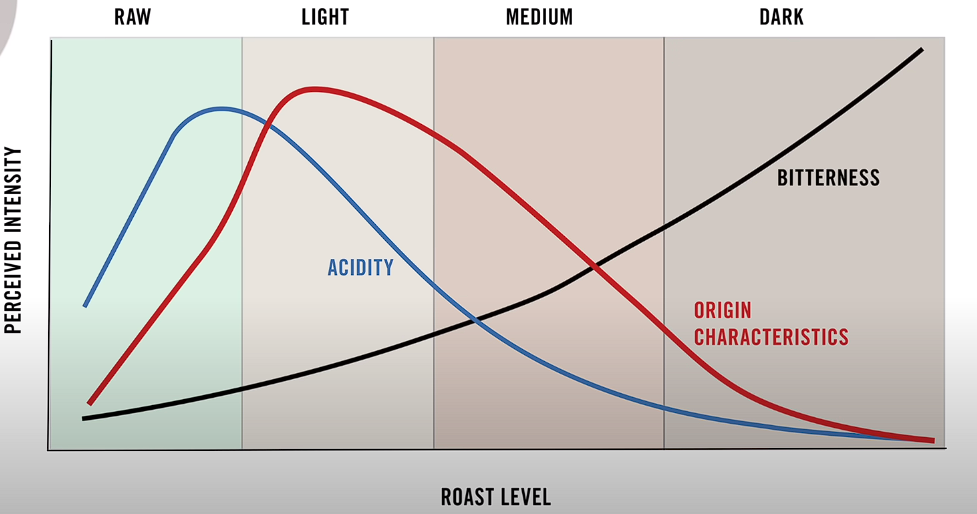
Origin characteristics, influenced by various factors such as soil type, climate, altitude, and post-harvest processing methods, contribute to the unique chemistry within the coffee seed. As the roasting process unfolds, distinct flavors are created based on the inherent qualities of the coffee. However, prolonged roasting diminishes these individualistic characteristics, leading to a more generic roast taste.
Peering into the Roasting Process: A Colorful Transformation
To gain deeper insights into the roasting process, let’s embark on a visual journey, observing the coffee beans’ transformation from raw to a dark roast. With our roasting machine as our guide, we witness the gradual color changes, which serve as an indicator of flavor development. The journey begins with the drying phase, transitioning from green to a pale yellow hue. Browning flavors emerge, signaling the initiation of the roasting chemistry.
The pivotal moment arrives at first crack, where the beans release built-up pressure, audibly crackling like popcorn. From this point onward, rapid and intricate browning reactions take place, influencing the flavor profile significantly. Although color changes may appear subtle, the flavor changes are substantial, impacting the coffee’s acidity, sweetness, and bitterness.
Decoding Roast Levels: From Light to Dark
Understanding the categorization of roast levels aids in navigating the coffee landscape. In the specialty coffee realm, light roasts exhibit flavors ranging from the beginning of the color spectrum to a specific point. Medium roasts encompass a broader range, while dark roasts are characterized by an intensified color and the presence of surface oil. Commercial roasting practices often extend further into the dark roast territory.
Unveiling Roast Profiles: The Art of Consistency
Roast profiles play a pivotal role in achieving consistent results in coffee roasting. Employing temperature probes and advanced software, roasters meticulously track and manipulate the temperature of the beans throughout the process. By varying the heat intensity and airflow, roasters strive to create desired flavor profiles. These profiles are tailored to specific coffees, often unique to individual roasting machines.

Quality Control and Brewing Methods
Roasters employ various quality control measures to ensure their coffees meet their desired standards. Beyond taste tests, they monitor roast profiles, roast loss percentages, and color measurements. These assessments enable them to gauge the success of their roasting endeavors and maintain consistency in their offerings.
Furthermore, the labeling of coffees for specific brewing methods, such as filter or espresso, communicates the intended flavor profile and roast characteristics. Espresso roasts are typically designed to facilitate extraction, while filter roasts allow for a more extended brewing process.
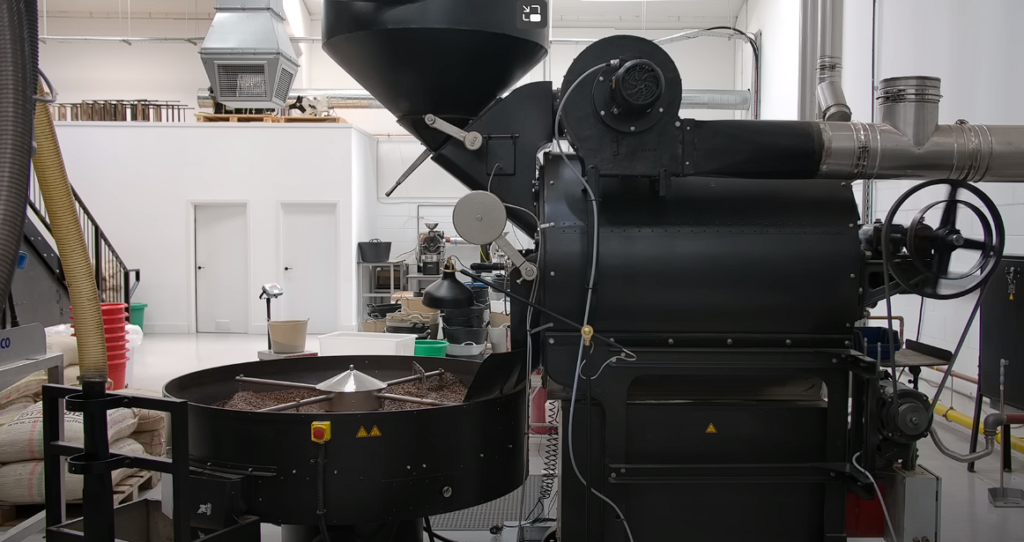
Roasting Machines: Drum Roasters, Hot Air Roasters, and Hybrid Roasters
Roasting machines come in different forms, each offering a unique approach to coffee roasting. Drum roasters, featuring a rotating drum, utilize convection, conduction, and radiant heat to roast coffee beans. Hot air roasters, on the other hand, rely solely on hot air to roast and agitate the beans, while hybrid roasters combine the benefits of a drum and hot air roaster.

Conclusion
The art of coffee roasting is a captivating blend of science, skill, and sensory exploration. From raw coffee seeds to flavorful roasted beans, the process unveils a symphony of tastes and aromas that delight coffee lovers worldwide. By understanding the impact of roasting on taste, appreciating roast levels and profiles, and recognizing the diverse range of roasting machines, we gain a deeper appreciation for the artistry behind every cup of coffee.
We hope this exploration has shed light on the intricacies of coffee roasting and kindled your curiosity. As you savor your next cup of coffee, take a moment to reflect on the remarkable journey those humble beans have undergone, transforming into a beverage that brings joy and warmth to our daily lives.